News
Marian Robinson, mother of Michelle Obama, dies at 86

- Texas’ 18th Congressional District Runoff: Amanda Edwards Deserves This Seat - December 18, 2025
- Turnout, Trust, and Ground Game: What Decided Houston’s Runoff Elections - December 14, 2025
- When Power Doesn’t Need Permission: Nigeria and the Collapse of a Gambian Coup Plot - December 14, 2025
Houston
Turnout, Trust, and Ground Game: What Decided Houston’s Runoff Elections

Low-turnout runoff races for Houston City Council and Houston Community College trustee seats revealed how message discipline, local credibility, and voter mobilization determined clear winners—and decisive losers.
The final ballots are counted, and Houston’s runoff elections have delivered clear outcomes in two closely watched local races, underscoring a familiar truth of municipal politics: in low-turnout elections, organization and credibility matter more than name recognition alone.
In the race for Houston City Council At-Large Position 4, Alejandra Salinas secured a decisive victory, winning 25,710 votes (59.27%) over former council member Dwight A. Boykins, who garnered 17,669 votes (40.73%). The margin was not accidental. Salinas ran a campaign tightly aligned with voter anxiety over public safety and infrastructure—two issues that consistently dominate Houston’s civic conversations. Her emphasis on keeping violent criminals off city streets and expanding Houston’s water supply spoke directly to quality-of-life concerns that resonate across districts, especially in an at-large contest where candidates must appeal to the city as a whole.
Salinas’ win reflects the advantage of message clarity. In a runoff, voters are not looking to be introduced to candidates—they are choosing between candidates they are already familiar with. Salinas presented herself as forward-looking and solutions-oriented, while Boykins, despite his experience and political history, struggled to reframe his candidacy beyond familiarity. In runoffs, nostalgia rarely outperforms momentum.
The second race—for Houston Community College District II trustee—followed a similar pattern. Renee Jefferson Patterson won with 2,497 votes (56.63%), defeating Kathleen “Kathy” Lynch Gunter, who received 1,912 votes (43.37%). Though the raw numbers were smaller, the dynamics were just as telling.
Patterson’s victory was powered by deep local ties and a clear institutional vision. As an HCC alumna, she effectively positioned herself as both a product and a steward of the system. Her pledge to expand the North Forest Campus and direct resources to Acres Home connected policy goals to place-based advocacy. In trustee races, voters often respond less to ideology and more to proximity—those who understand the campus, the students, and the neighborhood. Patterson checked all three boxes.
By contrast, Gunter’s loss highlights the challenge of overcoming a candidate with genuine community roots in a runoff scenario. Without a sharply differentiated message or a strong geographic base, turnout dynamics tend to favor candidates with existing neighborhood networks and direct institutional relevance.
What ultimately decided both races was not a surprise, but execution. Runoffs reward campaigns that can re-mobilize supporters, simplify their message, and convert familiarity into trust. Salinas and Patterson did exactly that. Their opponents, though credible, were unable to expand or energize their coalitions in a compressed electoral window.
The lesson from Houston’s runoff elections is straightforward but unforgiving: winners win because they align message, identity, and ground game. Losers lose because, in low-turnout contests, anything less than that alignment is insufficient.
- Texas’ 18th Congressional District Runoff: Amanda Edwards Deserves This Seat - December 18, 2025
- Turnout, Trust, and Ground Game: What Decided Houston’s Runoff Elections - December 14, 2025
- When Power Doesn’t Need Permission: Nigeria and the Collapse of a Gambian Coup Plot - December 14, 2025
Africa
Nigeria–Burkina Faso Rift: Military Power, Mistrust, and a Region Out of Balance

The brief detention of a Nigerian Air Force C-130 Hercules aircraft and its crew in Burkina Faso may have ended quietly, but it exposed a deeper rift shaped by mistrust, insecurity, and uneven military power in West Africa. What was officially a technical emergency landing quickly became a diplomatic and security flashpoint, reflecting not hostility between equals, but anxiety between unequally matched states navigating very different political realities.
On December 8, 2025, the Nigerian Air Force transport aircraft made an unscheduled landing in Bobo-Dioulasso while en route to Portugal. Nigerian authorities described the stop as a precautionary response to a technical fault—standard procedure under international aviation and military safety protocols. Burkina Faso acknowledged the emergency landing but emphasized that the aircraft had violated its airspace, prompting the temporary detention of 11 Nigerian personnel while investigations and repairs were conducted. Within days, the crew and aircraft were released, underscoring a professional, if tense, resolution.

Yet the symbolism mattered. In a Sahel region gripped by coups, insurgencies, and fragile legitimacy, airspace is not merely technical—it is political. Burkina Faso’s reaction reflected a state on edge, hyper-vigilant about sovereignty amid persistent internal threats. Nigeria’s response, measured and restrained, reflected confidence rooted in capacity.
The military imbalance between the two countries is stark. Nigeria fields one of Africa’s most formidable armed forces, with a tri-service structure that includes a large, well-equipped air force, a dominant regional navy, and a sizable army capable of sustained operations. The Nigerian Air Force operates fighter jets such as the JF-17 and F-7Ni, as well as A-29 Super Tucanos for counterinsurgency operations, heavy transport aircraft like the C-130, and an extensive helicopter fleet. This force is designed not only for internal security but for regional power projection and multinational operations.
Burkina Faso’s military, by contrast, is compact and narrowly focused. Its air arm relies on a limited number of light attack aircraft, including Super Tucanos, and a small helicopter fleet primarily dedicated to internal counterinsurgency. There is no navy, no strategic airlift capacity comparable to Nigeria’s, and limited logistical depth. The Burkinabè military is stretched thin, fighting multiple insurgent groups while also managing the political consequences of repeated military takeovers.
This imbalance shapes behavior. Nigeria’s military posture is institutional, outward-looking, and anchored in regional frameworks such as ECOWAS. Burkina Faso’s posture is defensive, reactive, and inward-facing. Where Nigeria seeks stability through deterrence and cooperation, Burkina Faso seeks survival amid constant internal pressure. That difference explains why a technical landing could be perceived as a “serious security breach” rather than a routine aviation incident.
The incident also illuminates why Burkina Faso continues to struggle to regain political balance. Repeated coups have eroded civilian institutions, fractured command structures, and blurred the line between governance and militarization. The armed forces are not just security actors; they are political stakeholders. This creates a cycle where insecurity justifies military rule, and military rule deepens insecurity by weakening democratic legitimacy and regional trust.
Nigeria, despite its own security challenges, has managed to avoid this spiral. Civilian control of the military remains intact, democratic transitions—however imperfect—continue, and its armed forces operate within a clearer constitutional framework. This stability enhances Nigeria’s regional credibility and amplifies its military superiority beyond hardware alone.
The C-130 episode did not escalate into confrontation precisely because of this asymmetry. Burkina Faso could assert sovereignty, but not sustain defiance. Nigeria could have asserted its capability, but chose restraint. In the end, professionalism prevailed.
Still, the rift lingers. It is not about one aircraft or one landing, but about two countries moving in different strategic directions. Nigeria stands as a regional anchor with superior military power and institutional depth. Burkina Faso remains a state searching for equilibrium—politically fragile, militarily constrained, and acutely sensitive to every perceived threat from the skies above.
- Texas’ 18th Congressional District Runoff: Amanda Edwards Deserves This Seat - December 18, 2025
- Turnout, Trust, and Ground Game: What Decided Houston’s Runoff Elections - December 14, 2025
- When Power Doesn’t Need Permission: Nigeria and the Collapse of a Gambian Coup Plot - December 14, 2025
News
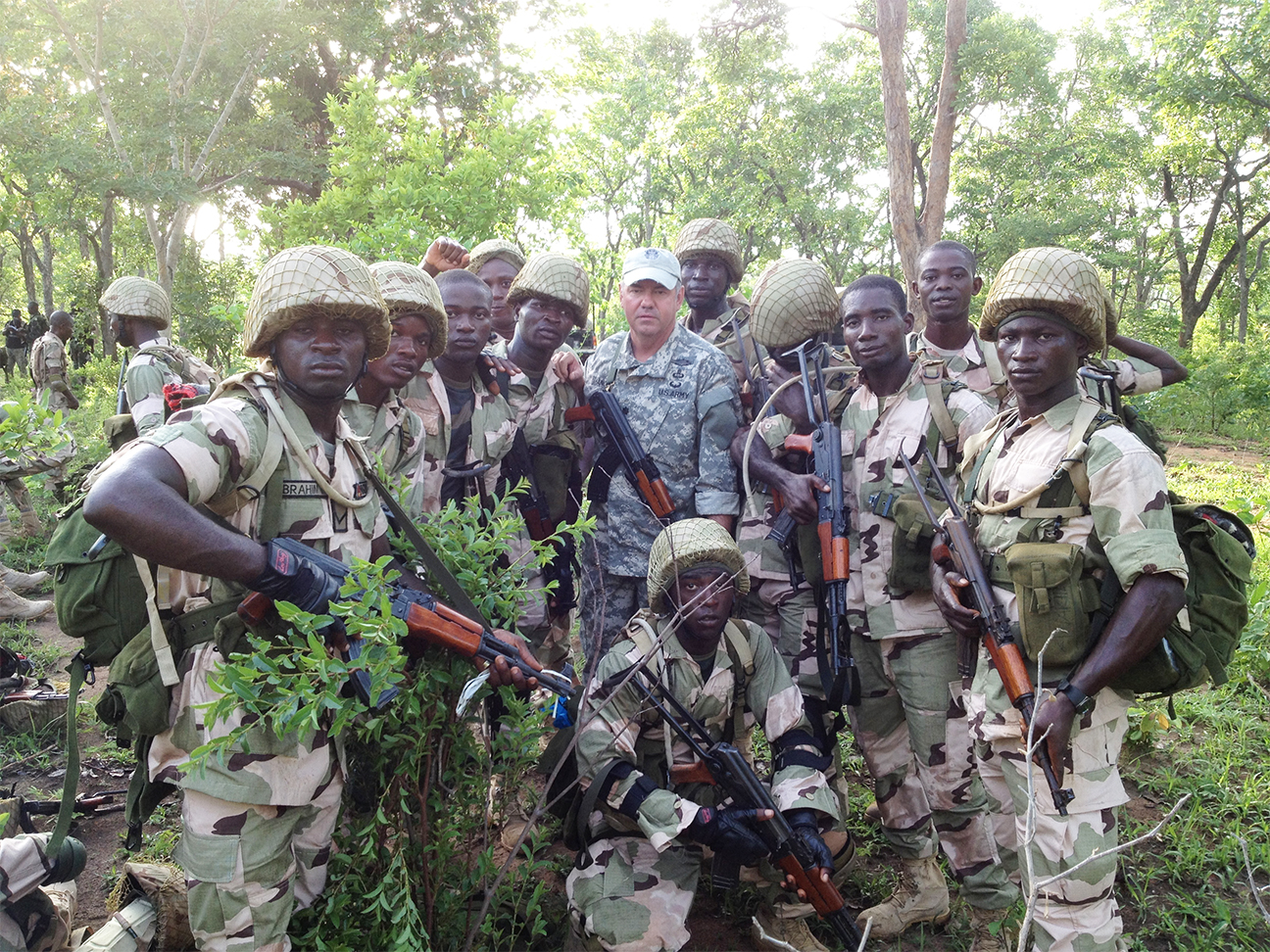
Bizarre Epstein files reference to Trump, Putin, and oral sex with ‘Bubba’ draws scrutiny in Congress

The latest tranche of emails from the estate of late convicted pedophile Jeffrey Epstein includes one that contains what appear to be references to President Donald Trump allegedly performing oral sex, raising questions the committee cannot answer until the Department of Justice turns over records it has withheld, says U.S. Rep. Robert Garcia, the top Democrat on the House Oversight Committee.
Garcia insists the Trump White House is helping block them.
In a Friday afternoon interview with The Advocate, the out California lawmaker responded to a 2018 exchange, which was included in the emails released, between Jeffrey Epstein and his brother, Mark Epstein. In that message, Mark wrote that because Jeffrey Epstein had said he was with former Trump adviser Steve Bannon, he should “ask him if Putin has the photos of Trump blowing Bubba.”
“Bubba” is a nickname former President Bill Clinton has been known by; however, the email does not clarify who Mark Epstein meant, and the context remains unclear.
- Texas’ 18th Congressional District Runoff: Amanda Edwards Deserves This Seat - December 18, 2025
- Turnout, Trust, and Ground Game: What Decided Houston’s Runoff Elections - December 14, 2025
- When Power Doesn’t Need Permission: Nigeria and the Collapse of a Gambian Coup Plot - December 14, 2025
-

 Anthony Obi Ogbo22 hours ago
Anthony Obi Ogbo22 hours agoTexas’ 18th Congressional District Runoff: Amanda Edwards Deserves This Seat
-

 Anthony Obi Ogbo5 days ago
Anthony Obi Ogbo5 days agoWhen Power Doesn’t Need Permission: Nigeria and the Collapse of a Gambian Coup Plot
-

 Anthony Obi Ogbo3 weeks ago
Anthony Obi Ogbo3 weeks agoBurna Boy, the Spotlight, and the Cost of Arrogance
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoBizarre Epstein files reference to Trump, Putin, and oral sex with ‘Bubba’ draws scrutiny in Congress
-

 Lifestyle1 month ago
Lifestyle1 month agoKaduna Governor Commissions Nigeria’s First 100-Building Prefabricated Housing Estate
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoUSDA head says ‘everyone’ on SNAP will now have to reapply
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoTrump orders Bondi to investigate Epstein’s ties to Clinton and other political foes
-

 Africa5 days ago
Africa5 days agoNigeria–Burkina Faso Rift: Military Power, Mistrust, and a Region Out of Balance