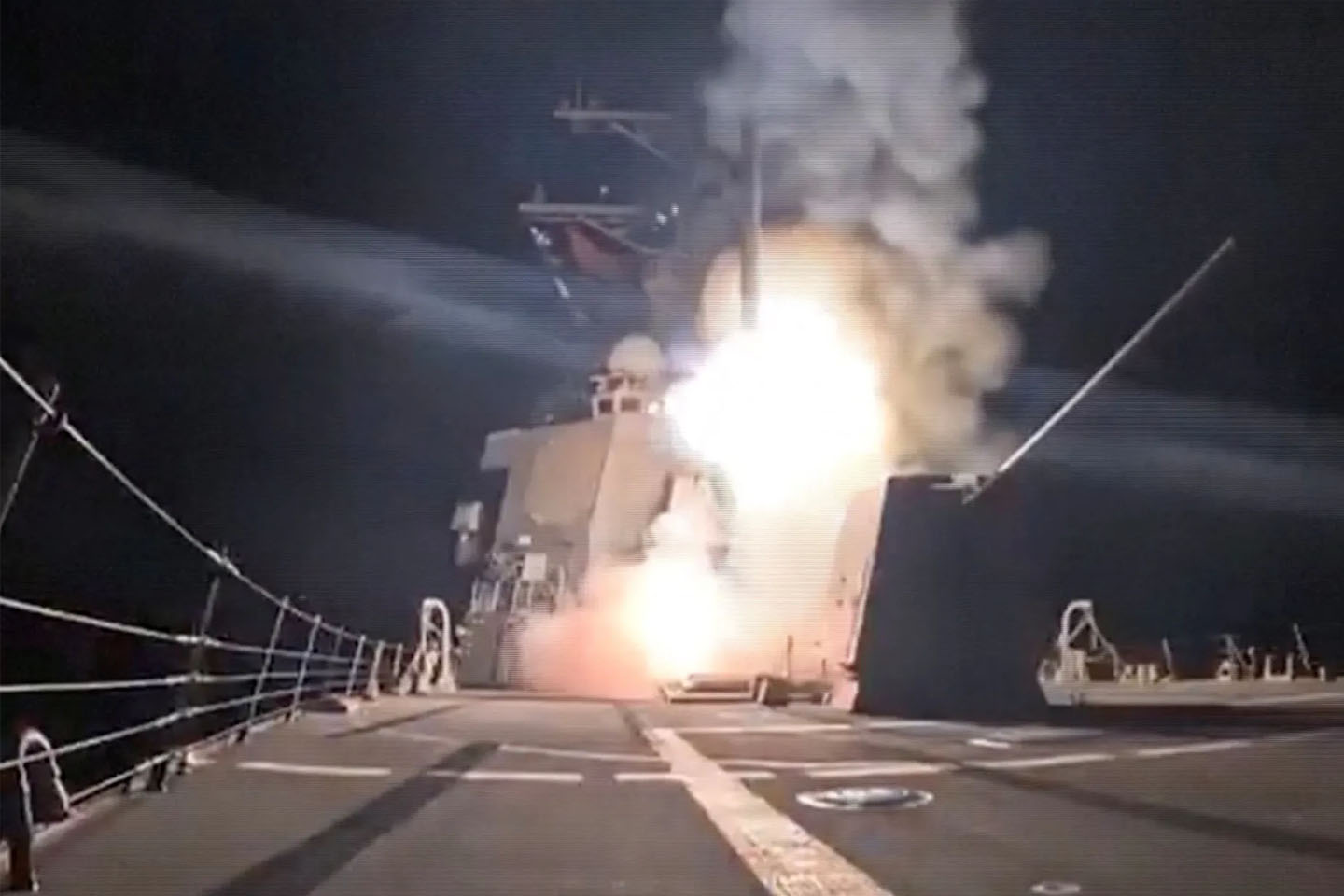
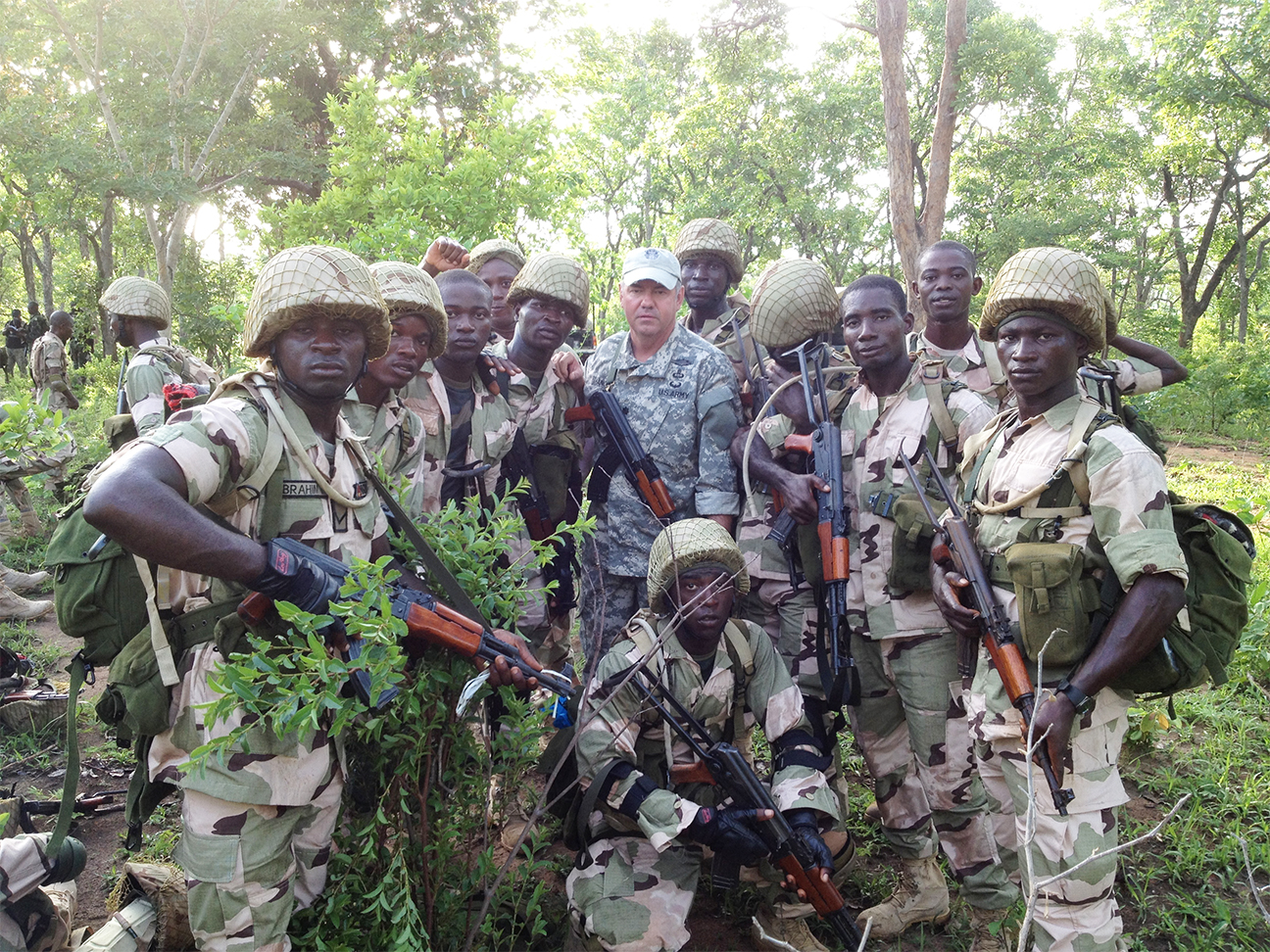
Top security officials, who confided in our correspondents, said the bombardment, which started in Katsina and Benue states would soon be extended to other states in the zones.
Recall that the President’s Senior Special Assistant on Media and Publicity Mallam Garba Shehu, in an interview with the Hausa Service of the BBC in March, said the President, Major General Muhammadu Buhari (retd.), had ordered crackdown on bandits terrorising farmers across the country.
Also, during his interview with Arise Television on Thursday, the President said he had ordered security agents to shoot bandits carrying AK47.
In Katsina State, The PUNCH gathered that the Nigerian army, the Nigerian Air Force and the police had increased attacks on the hideouts of bandits in various parts of the state especially in Batsari, Jibia, Sabuwa, Danmusa, Safana, Matazu, Kankara,Dandume, Dutsin-ma, Kurfi and Faskari local government areas, where bandits had been kidnapping farmers and other residents.
A top security source in the state said, “We now carry out operations on identified bandits’ hideouts in the state virtually on a daily basis and at anytime.
“At times, when you see fighter jets flying, it is either we are launching an attack against bandits or we are carrying out mop up operations.”
The Special Adviser to the state Governor on Security, Mallam Ahmad Katsina, had yet to respond to the SMS sent to him after futile efforts to get him on the phone.
But when contacted, the spokesman for the police in the state, Gambo Isah, said the command was “evolving strategies to ensure that all parts of the state are safe.”
The PUNCH learnt that troops of Operation Whirl Stroke had started flushing out armed herders and militias from their hideouts in Taraba, Nasarawa and Benue states.
A security official, who confided in one of our correspondents, said, “We have carried out operations in the Sankera axis (of Benue State). That is the reason farmers can return to their homes and begin farming activities.”
When asked if state government could direct the military to help in sending troops to protect farmers, the source said, “We don’t take order from the state government. What we are doing is to send troops to flash points, like in Sankera axis, farmers are already going back to their farms.”
In Sokoto State, the police have intensified patrols of villages that are prone to bandits’ attacks.
The areas include Sabon Birni, Isa, Rabah and Goronyo local government areas.
But unlike in Katsina, military has yet to begin operations aimed at flushing out bandits from the areas.
A police source stated, “What we do is a routine patrol of areas under the jurisdiction of each divisional police officer. We have sensitised the villagers to quickly send distress calls in the face of attacks.”
On its part, , the Zamfara State Police Command said it had deployed more policemen in areas that were prone to bandits’ attacks.
Speaking to one of our correspondents on the phone, the spokesperson for the command, Mohammed Shehu, said, “The police, in collaboration with other security agencies, have mapped out strategies to ensure the return of farmers to their farms.”
He maintained that ,the command would engage the services of the repentant bandits as well as other locals who would assist in the fight against banditry.
In Kebbi State, vigilantes who were assisting in providing security suffered heavy casualties when bandits attacked some communities a few weeks ago.
As Kebbi State farmers battled problems of bandits, the Miyetti Allah Cattle Breeders Association of Nigeria and the Benue State Government on Tuesday disagreed over a military operation at a boundary between the state and Nasarawa State.
There was a report on Tuesday that military aircraft killed over 1,000 cows during multiple attacks on Fulani settlements in Keana and Doma local government areas of Nasarawa State.
According to the report, victims said the military launched the attacks between June 10 and June 13.
But on Tuesday, while the Benue State Government said no human life or cow was lost in the attack, MACBAN said 500 cows were killed.
NAF bombs killed 500 cows, 200 missing – Miyetti Allah
The MACBAN Acting Chairman in Nasarawa State, Bala Dabo, in an interview with one of our correspondents, expressed concern about the military operation.
He said 500 cows were killed during the military operation in the Kuduku community of the Keana Local Government Area and some parts of the Doma Local Government Area.
He alleged that two military aircraft that were deployed in Fulani settlements threw bombs, causing the death of the cows.
The MACBAN leader said that there was a deliberate plan to send the Fulani into extinction following the anti-open grazing law passed by some states in the country.
He stated, “The anti-grazing law in Benue State is meant to force the Fulani into extinction. We appeal to the Federal Government to rise up to the challenge and salvage our people.
“There is no justification for gunships to come to Nasarawa territory and kill cows. We are peace-loving people and not troublemakers.”
“The cows are our sources of livelihood. We are in pain at the moment and we are calling for help from Nigerians. We had just returned from grazing when the aircraft came and killed them around 6pm on Sunday.
“The cows killed were between 450 and 500. Some of them got injured. There are some of the cows that ran into the bush and up till now, we are still looking for them. About 200 cows are missing at the moment. I also got information that the herdsmen controlling the cows were also affected by the bombs thrown by the military.”
But the Nasarawa State Government said the incident had not been confirmed. It assured that an investigation would be carried out to ascertain the actual cause of the issue and possibly find a lasting solution to it.
The state Commissioner for Information, Culture and Tourism, Dogo Shammah, who stated these in an interview with one of our correspondents on Tuesday in Lafia, said, “We heard something of that nature. We will investigate the issue to know what exactly transpired. I assure you that government will do everything possible to address the issue and restore normalcy in the affected area”
No cow, human being killed in military operation, Benue insists
But the Benue State Government denied allegations against the state Governor, Samuel Ortom, on the anti-open grazing law.
The state Commissioner for Information, Culture and Tourism, Mrs Ngunan Addingi, in an interview with journalists in Makurdi on Tuesday, said the military was only carrying out operations at the boundary between Benue and Nasarawa states where terrorists had sacked and taken over communities.
She stated, “No farming activity takes place in the affected communities any longer. The military was only performing its duty of flushing out terrorists who wield AK47 and occupy the forests from where they launch attacks on innocent people.
“In the aerial surveillance carried out in border communities of Benue and Nasarawa states by Operation Whirl Stroke, no human life or cow was lost,” Addingi said.
Recall that Ortom had three weeks ago allayed the fears of people of the state. He said the aerial surveillance that would be carried out by the military in parts of the state was to flush out criminals and bandits.