Nigeria
Insurgency ‘ll Persist Until Nigerians Are Gainfully Engaged – Lukman

- When Air Power Becomes a Christmas Performance: The Illusion of Success in Trump’s Nigerian Strike - December 28, 2025
- Burna Boy, the Spotlight, and the Cost of Arrogance - November 27, 2025
- Billionaires Conclave USA Brings Career Wealth Masterclass to Houston with Dr. Olumide Emmanuel - July 12, 2025
Africa
U.S. Signals More Strikes in Nigeria as Abuja Confirms Joint Military Campaign
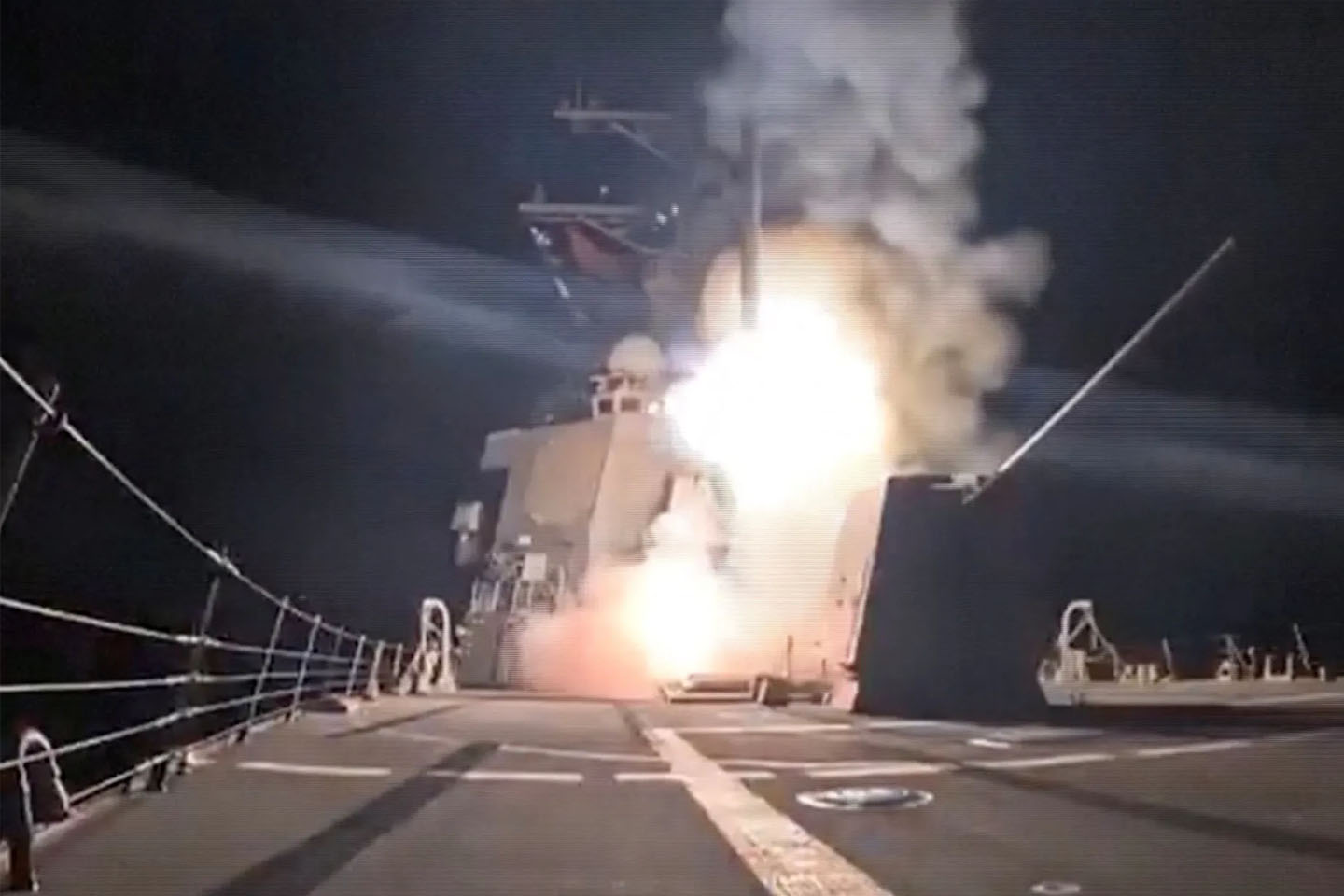

The United States has warned that further airstrikes against Islamic State targets in north-western Nigeria are imminent, as Nigerian officials confirmed that recent attacks were part of coordinated operations between both countries.
The warning came hours after U.S. forces struck militant camps in Sokoto State, an operation President Donald Trump publicly framed as a response to what he described as the killing of Christians in Nigeria. U.S. Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth said the strikes were only the beginning.
“The president was clear last month: the killing of innocent Christians in Nigeria (and elsewhere) must end,” Hegseth wrote on X. “The Pentagon is always ready, so ISIS found out tonight—on Christmas. More to come. Grateful for Nigerian government support & cooperation.”
Nigeria’s foreign minister, Yusuf Tuggar, confirmed on Friday that the strikes were carried out as part of “joint ongoing operations,” pushing back against earlier tensions sparked by Trump’s public criticism of Nigeria’s handling of insecurity.
The airstrikes followed a brief diplomatic rift after Trump accused Nigeria’s government of failing to protect Christians from militant violence. Nigerian officials responded by reiterating that extremist groups in the country target both Christians and Muslims, and that the conflict is driven by insurgency and criminality rather than religious persecution.
Speaking to Channels Television, Tuggar said Nigeria provided intelligence support for the strikes in Sokoto and described close coordination with Washington. He said he spoke with U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio for nearly 20 minutes before briefing President Bola Tinubu and receiving approval to proceed, followed by another call with Rubio to finalize arrangements.
“We have been working closely with the Americans,” Tuggar said. “This is what we’ve always been hoping for—to work together to combat terrorism and stop the deaths of innocent Nigerians. It’s a collaborative effort.”
U.S. Africa Command later confirmed that the strikes were conducted in coordination with Nigerian authorities. An earlier statement, later removed, had suggested the operation was carried out at Nigeria’s request.
Trump, speaking in an interview with Politico, said the operation had originally been scheduled for Wednesday but was delayed at his instruction. “They were going to do it earlier,” he said. “And I said, ‘Nope, let’s give a Christmas present.’ They didn’t think that was coming, but we hit them hard. Every camp got decimated.”
Neither the U.S. nor Nigerian authorities have disclosed casualty figures or confirmed whether militants were killed. Tuggar, when asked whether additional strikes were planned, said only: “You can call it a new phase of an old conflict. For us, this is ongoing.”
Nigeria is officially a secular state, with a population split roughly between Muslims and Christians. While violence against Christian communities has drawn increasing attention from religious conservatives in the United States, Nigeria’s government maintains that extremist groups operate without regard to faith, attacking civilians across religious lines.
Trump’s public rhetoric contrasts with his 2024 campaign messaging, in which he cast himself as a “candidate of peace” who would pull the United States out of what he called endless foreign wars. Yet his second term has already seen expanded U.S. military action abroad, including strikes in Yemen, Iran, and Syria, as well as a significant military buildup in the Caribbean directed at Venezuela.
On the ground in Sokoto State, residents of Jabo village—near one of the strike sites—reported panic and confusion as missiles hit nearby areas. Local residents said no casualties had been recorded, but security forces quickly sealed off the area.
“As it approached our area, the heat became intense,” Abubakar Sani told the Associated Press. “The government should take appropriate measures to protect us. We have never experienced anything like this before.”
Another resident, farmer Sanusi Madabo, said the night sky glowed red for hours. “It was almost like daytime,” he said. “We only learned later that it was a U.S. airstrike.”
For now, both Washington and Abuja are projecting unity. Whether the strikes mark a sustained shift in strategy—or another brief escalation in a long war—remains unclear.
- When Air Power Becomes a Christmas Performance: The Illusion of Success in Trump’s Nigerian Strike - December 28, 2025
- Burna Boy, the Spotlight, and the Cost of Arrogance - November 27, 2025
- Billionaires Conclave USA Brings Career Wealth Masterclass to Houston with Dr. Olumide Emmanuel - July 12, 2025
Africa
Nigeria–Burkina Faso Rift: Military Power, Mistrust, and a Region Out of Balance

The brief detention of a Nigerian Air Force C-130 Hercules aircraft and its crew in Burkina Faso may have ended quietly, but it exposed a deeper rift shaped by mistrust, insecurity, and uneven military power in West Africa. What was officially a technical emergency landing quickly became a diplomatic and security flashpoint, reflecting not hostility between equals, but anxiety between unequally matched states navigating very different political realities.
On December 8, 2025, the Nigerian Air Force transport aircraft made an unscheduled landing in Bobo-Dioulasso while en route to Portugal. Nigerian authorities described the stop as a precautionary response to a technical fault—standard procedure under international aviation and military safety protocols. Burkina Faso acknowledged the emergency landing but emphasized that the aircraft had violated its airspace, prompting the temporary detention of 11 Nigerian personnel while investigations and repairs were conducted. Within days, the crew and aircraft were released, underscoring a professional, if tense, resolution.

Yet the symbolism mattered. In a Sahel region gripped by coups, insurgencies, and fragile legitimacy, airspace is not merely technical—it is political. Burkina Faso’s reaction reflected a state on edge, hyper-vigilant about sovereignty amid persistent internal threats. Nigeria’s response, measured and restrained, reflected confidence rooted in capacity.
The military imbalance between the two countries is stark. Nigeria fields one of Africa’s most formidable armed forces, with a tri-service structure that includes a large, well-equipped air force, a dominant regional navy, and a sizable army capable of sustained operations. The Nigerian Air Force operates fighter jets such as the JF-17 and F-7Ni, as well as A-29 Super Tucanos for counterinsurgency operations, heavy transport aircraft like the C-130, and an extensive helicopter fleet. This force is designed not only for internal security but for regional power projection and multinational operations.
Burkina Faso’s military, by contrast, is compact and narrowly focused. Its air arm relies on a limited number of light attack aircraft, including Super Tucanos, and a small helicopter fleet primarily dedicated to internal counterinsurgency. There is no navy, no strategic airlift capacity comparable to Nigeria’s, and limited logistical depth. The Burkinabè military is stretched thin, fighting multiple insurgent groups while also managing the political consequences of repeated military takeovers.
This imbalance shapes behavior. Nigeria’s military posture is institutional, outward-looking, and anchored in regional frameworks such as ECOWAS. Burkina Faso’s posture is defensive, reactive, and inward-facing. Where Nigeria seeks stability through deterrence and cooperation, Burkina Faso seeks survival amid constant internal pressure. That difference explains why a technical landing could be perceived as a “serious security breach” rather than a routine aviation incident.
The incident also illuminates why Burkina Faso continues to struggle to regain political balance. Repeated coups have eroded civilian institutions, fractured command structures, and blurred the line between governance and militarization. The armed forces are not just security actors; they are political stakeholders. This creates a cycle where insecurity justifies military rule, and military rule deepens insecurity by weakening democratic legitimacy and regional trust.
Nigeria, despite its own security challenges, has managed to avoid this spiral. Civilian control of the military remains intact, democratic transitions—however imperfect—continue, and its armed forces operate within a clearer constitutional framework. This stability enhances Nigeria’s regional credibility and amplifies its military superiority beyond hardware alone.
The C-130 episode did not escalate into confrontation precisely because of this asymmetry. Burkina Faso could assert sovereignty, but not sustain defiance. Nigeria could have asserted its capability, but chose restraint. In the end, professionalism prevailed.
Still, the rift lingers. It is not about one aircraft or one landing, but about two countries moving in different strategic directions. Nigeria stands as a regional anchor with superior military power and institutional depth. Burkina Faso remains a state searching for equilibrium—politically fragile, militarily constrained, and acutely sensitive to every perceived threat from the skies above.
- When Air Power Becomes a Christmas Performance: The Illusion of Success in Trump’s Nigerian Strike - December 28, 2025
- Burna Boy, the Spotlight, and the Cost of Arrogance - November 27, 2025
- Billionaires Conclave USA Brings Career Wealth Masterclass to Houston with Dr. Olumide Emmanuel - July 12, 2025
Lifestyle
Kaduna Governor Commissions Nigeria’s First 100-Building Prefabricated Housing Estate
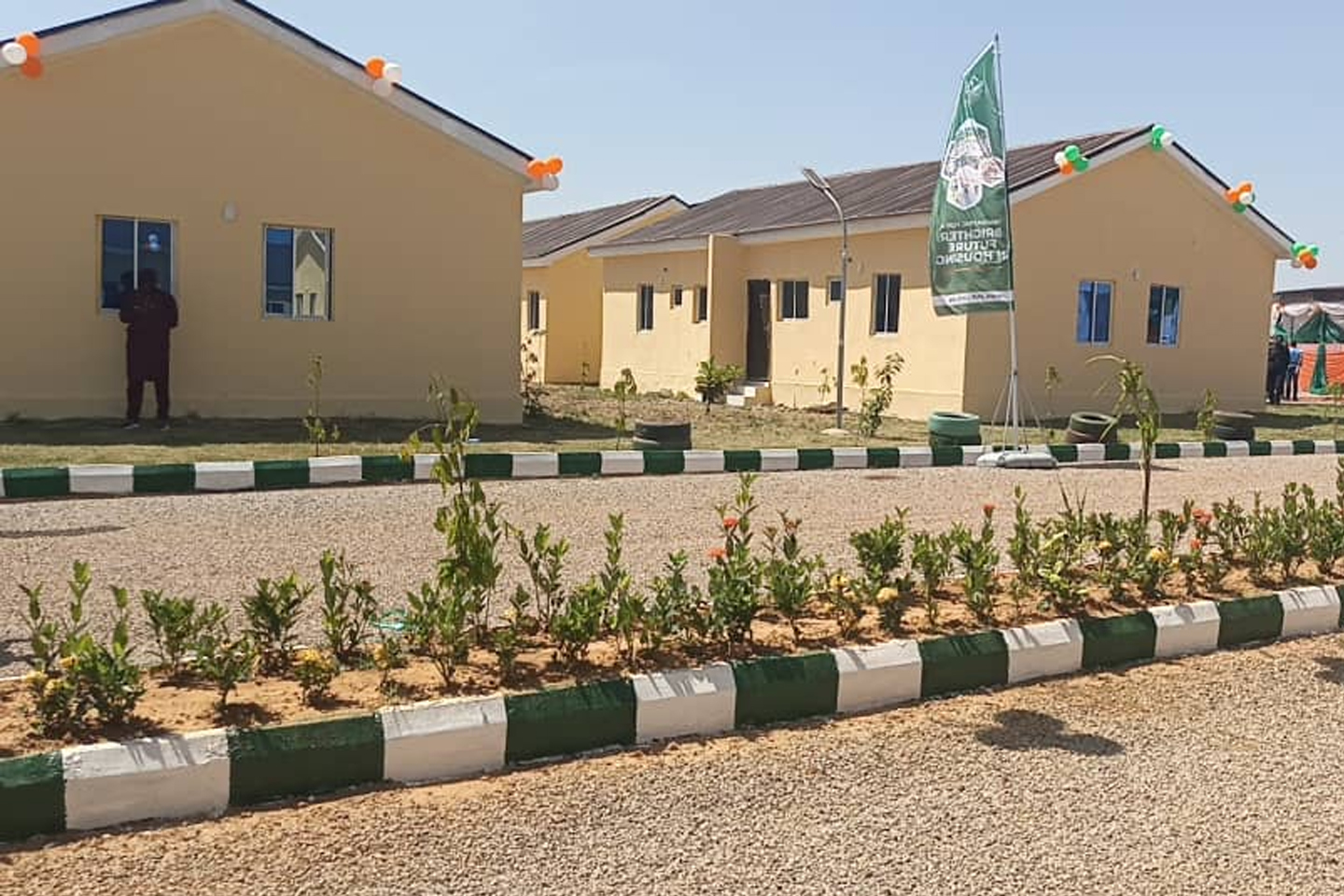

Kaduna, Nigeria – November 6, 2025 — In a major milestone for Nigeria’s housing sector, the Governor of Kaduna State has commissioned a 100-unit mass housing estate developed by Family Homes and executed by Karmod Nigeria, marking the first-ever large-scale prefabricated housing project in the country.
Completed in under six months, the innovative project demonstrates the power of modern prefabricated construction to deliver high-quality, affordable homes at record speed — a sharp contrast to traditional building methods that often take years.
Each of the 100 units in the estate is designed for a lifespan exceeding 50 years with routine maintenance. The development features tarred access roads, efficient drainage systems, clean water supply, and steady electricity, ensuring a modern and comfortable living environment for residents.
According to Family Homes, the project represents a new era in Nigeria’s mass housing delivery, proving that cutting-edge technology can accelerate the provision of sustainable and cost-effective homes for Nigerians.
“With prefabricated technology, we can drastically reduce construction time while maintaining top-quality standards,” said a spokesperson for Family Homes. “This project is a clear demonstration of what’s possible when innovation meets commitment to solving Nigeria’s housing deficit.”
Reinforcing this commitment, Governor Uba Sani of Kaduna State emphasized the alignment between the initiative and the state’s broader vision for affordable housing.
“The Family Homes Funds Social Housing Project aligns with our administration’s commitment to the provision of affordable houses for Kaduna State citizens. Access to safe, affordable and secure housing is the foundation of human dignity. We have been partnering with local and international investors to frontally address our housing deficit,” he said.
Also speaking at the event, Mr. Ademola Adebise, Chairman of Family Homes Funds Limited, noted that the project embodies inclusivity and social progress.
“The Social Housing Project also reflects our shared vision of inclusive growth, where affordable housing becomes a foundation for economic participation and improved quality of life.”
Karmod Nigeria, the technical partner behind the project, utilized its extensive expertise in prefabricated technology to localize the process, employing local artisans and materials to enhance community participation and job creation.
Industry experts have described the Kaduna project as a blueprint for future housing initiatives nationwide, capable of addressing the country’s housing shortfall more efficiently and sustainably.
With this pioneering development, Kaduna State takes a leading role in introducing modern housing technologies that promise to reshape Nigeria’s urban landscape.
- When Air Power Becomes a Christmas Performance: The Illusion of Success in Trump’s Nigerian Strike - December 28, 2025
- Burna Boy, the Spotlight, and the Cost of Arrogance - November 27, 2025
- Billionaires Conclave USA Brings Career Wealth Masterclass to Houston with Dr. Olumide Emmanuel - July 12, 2025