News
Haiti deportations justified because of Covid, Biden homeland secretary says

- From Threats to Partnership: How Diplomacy Repositioned Nigeria in Washington - January 13, 2026
- Burbank Marriage Unravels After Woman Allegedly Used Tracking Devices to Monitor Husband - December 27, 2025
- U.S. Signals More Strikes in Nigeria as Abuja Confirms Joint Military Campaign - December 27, 2025
Lifestyle
Burbank Marriage Unravels After Woman Allegedly Used Tracking Devices to Monitor Husband

Burbank, Calif. — What began as a seemingly happy two-year marriage ended in confrontation and police involvement after a Burbank woman allegedly used multiple electronic tracking devices to monitor her husband’s movements, authorities and sources familiar with the situation said.

According to information obtained by this outlet, the marriage between Amos and Yolanda deteriorated after Yolanda allegedly placed Apple AirTags, Tile trackers, and a GPS tracking device on Amos’ vehicle and personal belongings without his knowledge. The devices reportedly allowed her to monitor his location in real time and reconstruct his daily movements across the city.

Friends of the couple said the marriage appeared stable during its early years, with the pair often seen together at community events and social gatherings. However, tensions reportedly escalated when Yolanda began confronting Amos about his whereabouts, referencing locations and timelines he had not shared with her.
The situation reached a breaking point when Yolanda allegedly tracked Amos to an apartment complex in Burbank, where she believed he had gone without informing her. Sources say she arrived at the location shortly after he did, leading to a heated confrontation in the parking area of the building. Neighbors, alarmed by raised voices, contacted local authorities.
Burbank police responded to the scene and separated the parties. While no arrests were immediately announced, the incident marked the effective end of the couple’s marriage, according to individuals close to Amos.
Legal experts note that the unauthorized use of tracking devices may raise serious privacy and stalking concerns under California law, depending on intent and consent. Law enforcement officials have not publicly disclosed whether an investigation remains ongoing.
The case underscores growing concerns about the misuse of consumer tracking technology, originally designed to help locate lost items, but increasingly implicated in domestic disputes and surveillance-related allegations.
As of publication, neither Amos nor Yolanda had publicly commented on the incident.
- From Threats to Partnership: How Diplomacy Repositioned Nigeria in Washington - January 13, 2026
- Burbank Marriage Unravels After Woman Allegedly Used Tracking Devices to Monitor Husband - December 27, 2025
- U.S. Signals More Strikes in Nigeria as Abuja Confirms Joint Military Campaign - December 27, 2025
Africa
U.S. Signals More Strikes in Nigeria as Abuja Confirms Joint Military Campaign

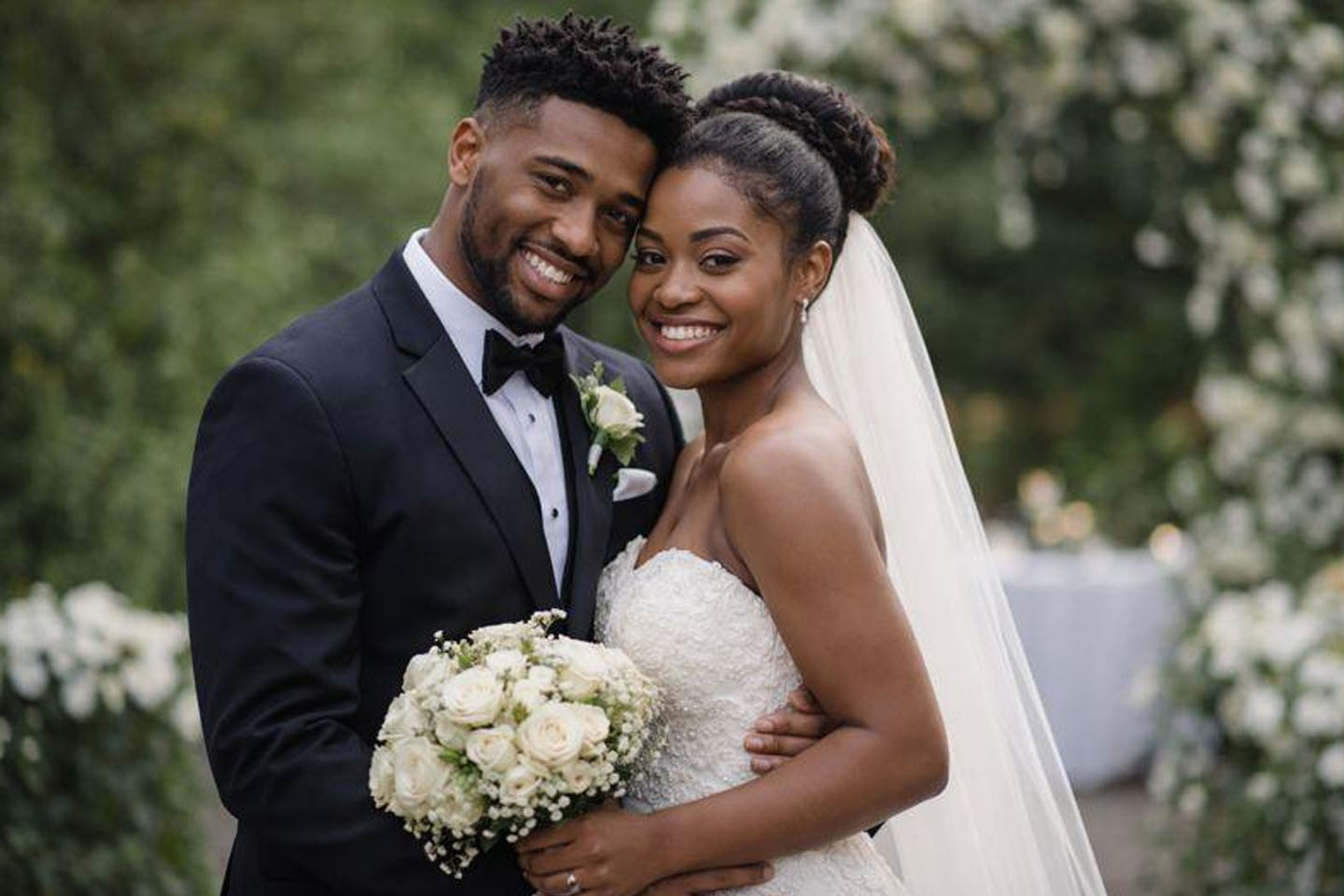
The United States has warned that further airstrikes against Islamic State targets in north-western Nigeria are imminent, as Nigerian officials confirmed that recent attacks were part of coordinated operations between both countries.
The warning came hours after U.S. forces struck militant camps in Sokoto State, an operation President Donald Trump publicly framed as a response to what he described as the killing of Christians in Nigeria. U.S. Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth said the strikes were only the beginning.
“The president was clear last month: the killing of innocent Christians in Nigeria (and elsewhere) must end,” Hegseth wrote on X. “The Pentagon is always ready, so ISIS found out tonight—on Christmas. More to come. Grateful for Nigerian government support & cooperation.”
Nigeria’s foreign minister, Yusuf Tuggar, confirmed on Friday that the strikes were carried out as part of “joint ongoing operations,” pushing back against earlier tensions sparked by Trump’s public criticism of Nigeria’s handling of insecurity.
The airstrikes followed a brief diplomatic rift after Trump accused Nigeria’s government of failing to protect Christians from militant violence. Nigerian officials responded by reiterating that extremist groups in the country target both Christians and Muslims, and that the conflict is driven by insurgency and criminality rather than religious persecution.
Speaking to Channels Television, Tuggar said Nigeria provided intelligence support for the strikes in Sokoto and described close coordination with Washington. He said he spoke with U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio for nearly 20 minutes before briefing President Bola Tinubu and receiving approval to proceed, followed by another call with Rubio to finalize arrangements.
“We have been working closely with the Americans,” Tuggar said. “This is what we’ve always been hoping for—to work together to combat terrorism and stop the deaths of innocent Nigerians. It’s a collaborative effort.”
U.S. Africa Command later confirmed that the strikes were conducted in coordination with Nigerian authorities. An earlier statement, later removed, had suggested the operation was carried out at Nigeria’s request.
Trump, speaking in an interview with Politico, said the operation had originally been scheduled for Wednesday but was delayed at his instruction. “They were going to do it earlier,” he said. “And I said, ‘Nope, let’s give a Christmas present.’ They didn’t think that was coming, but we hit them hard. Every camp got decimated.”
Neither the U.S. nor Nigerian authorities have disclosed casualty figures or confirmed whether militants were killed. Tuggar, when asked whether additional strikes were planned, said only: “You can call it a new phase of an old conflict. For us, this is ongoing.”
Nigeria is officially a secular state, with a population split roughly between Muslims and Christians. While violence against Christian communities has drawn increasing attention from religious conservatives in the United States, Nigeria’s government maintains that extremist groups operate without regard to faith, attacking civilians across religious lines.
Trump’s public rhetoric contrasts with his 2024 campaign messaging, in which he cast himself as a “candidate of peace” who would pull the United States out of what he called endless foreign wars. Yet his second term has already seen expanded U.S. military action abroad, including strikes in Yemen, Iran, and Syria, as well as a significant military buildup in the Caribbean directed at Venezuela.
On the ground in Sokoto State, residents of Jabo village—near one of the strike sites—reported panic and confusion as missiles hit nearby areas. Local residents said no casualties had been recorded, but security forces quickly sealed off the area.
“As it approached our area, the heat became intense,” Abubakar Sani told the Associated Press. “The government should take appropriate measures to protect us. We have never experienced anything like this before.”
Another resident, farmer Sanusi Madabo, said the night sky glowed red for hours. “It was almost like daytime,” he said. “We only learned later that it was a U.S. airstrike.”
For now, both Washington and Abuja are projecting unity. Whether the strikes mark a sustained shift in strategy—or another brief escalation in a long war—remains unclear.
- From Threats to Partnership: How Diplomacy Repositioned Nigeria in Washington - January 13, 2026
- Burbank Marriage Unravels After Woman Allegedly Used Tracking Devices to Monitor Husband - December 27, 2025
- U.S. Signals More Strikes in Nigeria as Abuja Confirms Joint Military Campaign - December 27, 2025
Houston
Turnout, Trust, and Ground Game: What Decided Houston’s Runoff Elections

Low-turnout runoff races for Houston City Council and Houston Community College trustee seats revealed how message discipline, local credibility, and voter mobilization determined clear winners—and decisive losers.
The final ballots are counted, and Houston’s runoff elections have delivered clear outcomes in two closely watched local races, underscoring a familiar truth of municipal politics: in low-turnout elections, organization and credibility matter more than name recognition alone.
In the race for Houston City Council At-Large Position 4, Alejandra Salinas secured a decisive victory, winning 25,710 votes (59.27%) over former council member Dwight A. Boykins, who garnered 17,669 votes (40.73%). The margin was not accidental. Salinas ran a campaign tightly aligned with voter anxiety over public safety and infrastructure—two issues that consistently dominate Houston’s civic conversations. Her emphasis on keeping violent criminals off city streets and expanding Houston’s water supply spoke directly to quality-of-life concerns that resonate across districts, especially in an at-large contest where candidates must appeal to the city as a whole.
Salinas’ win reflects the advantage of message clarity. In a runoff, voters are not looking to be introduced to candidates—they are choosing between candidates they are already familiar with. Salinas presented herself as forward-looking and solutions-oriented, while Boykins, despite his experience and political history, struggled to reframe his candidacy beyond familiarity. In runoffs, nostalgia rarely outperforms momentum.
The second race—for Houston Community College District II trustee—followed a similar pattern. Renee Jefferson Patterson won with 2,497 votes (56.63%), defeating Kathleen “Kathy” Lynch Gunter, who received 1,912 votes (43.37%). Though the raw numbers were smaller, the dynamics were just as telling.
Patterson’s victory was powered by deep local ties and a clear institutional vision. As an HCC alumna, she effectively positioned herself as both a product and a steward of the system. Her pledge to expand the North Forest Campus and direct resources to Acres Home connected policy goals to place-based advocacy. In trustee races, voters often respond less to ideology and more to proximity—those who understand the campus, the students, and the neighborhood. Patterson checked all three boxes.
By contrast, Gunter’s loss highlights the challenge of overcoming a candidate with genuine community roots in a runoff scenario. Without a sharply differentiated message or a strong geographic base, turnout dynamics tend to favor candidates with existing neighborhood networks and direct institutional relevance.
What ultimately decided both races was not a surprise, but execution. Runoffs reward campaigns that can re-mobilize supporters, simplify their message, and convert familiarity into trust. Salinas and Patterson did exactly that. Their opponents, though credible, were unable to expand or energize their coalitions in a compressed electoral window.
The lesson from Houston’s runoff elections is straightforward but unforgiving: winners win because they align message, identity, and ground game. Losers lose because, in low-turnout contests, anything less than that alignment is insufficient.
- From Threats to Partnership: How Diplomacy Repositioned Nigeria in Washington - January 13, 2026
- Burbank Marriage Unravels After Woman Allegedly Used Tracking Devices to Monitor Husband - December 27, 2025
- U.S. Signals More Strikes in Nigeria as Abuja Confirms Joint Military Campaign - December 27, 2025